Contents
Summary
ERP Business is a full-featured, SaaS-ready PHP script that helps small businesses manage sales, purchases, HR, inventory, and accounting from one dashboard. Ideal for shops, wholesalers, and service providers. 👉 Buy ERP Business on CodeCanyon
What Is ERP Business – ERP Solution?
ERP Business is a powerful PHP-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) script built for small and medium-sized businesses. It offers modules for sales, purchases, stock, customer management, accounting, and human resources, all integrated into a single platform.
Designed for easy deployment and scalability, it allows businesses to digitize their operations without depending on expensive third-party software or subscriptions.
Who Is It For?
-
Small business owners and shopkeepers
-
Wholesalers and trading companies
-
Freelancers building ERP solutions for clients
-
SaaS founders offering ERP services
-
Developers needing a full ERP backend
👉 Visit ERP Business on CodeCanyon
Key Features of ERP Business
-
Sales and purchase order management with invoice generation
-
Inventory and stock control with product tracking
-
Customer and supplier database with contact details
-
HR module for employee management, salary, and attendance
-
Accounting and financial reports
-
Multi-user support with role-based access control
-
Point of Sale (POS) system included
-
Export reports to PDF/Excel
-
Multi-currency and multi-language support
-
Clean admin dashboard with charts and statistics
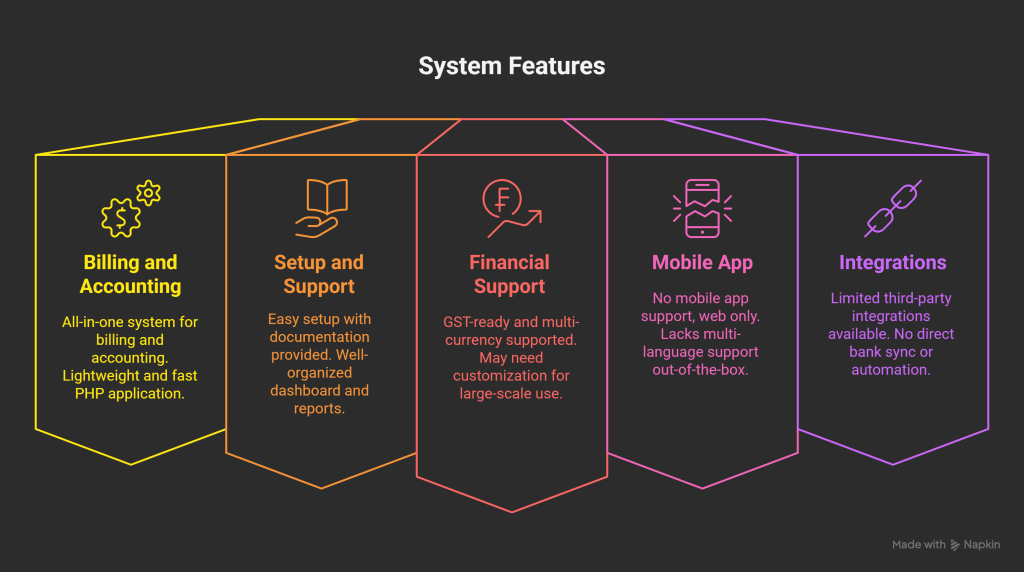
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| All-in-one ERP script for small businesses | No mobile app included |
| POS system and HR module built-in | Limited third-party integrations |
| Clean interface and easy navigation | May require technical skills for customization |
| SaaS-ready PHP script with licensing flexibility | UI is functional but not very modern |
| Great value for the price | Not ideal for very large or enterprise-level orgs |
Installation and Setup Guide
Installation Steps:
-
Upload the script files to your web hosting (via FTP or cPanel)
-
Create a new MySQL database
-
Run the installation wizard from your browser
-
Set your base URL, admin account, and company settings
System Requirements:
-
PHP version: 7.2 or higher
-
MySQL 5.6+
-
Apache/Nginx server
-
Enabled extensions: PDO, GD, Mbstring, OpenSSL, Fileinfo
📄 Documentation: (Included in the CodeCanyon download package)
Pricing and License Options
| License Type | Price (Approx.) | Usage Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Regular License | $49 | For one business or client use, no resale |
| Extended License | $399 | Use as a SaaS, charge users, or resell |
👉 Buy ERP Business on CodeCanyon
Final Verdict – Is It Worth Buying?
ERP Business is a complete, reliable ERP PHP script for businesses looking to digitize their operations affordably. It delivers real value with essential modules like sales, stock, HR, and accounting without monthly fees.
Buy it if:
You’re running a shop, wholesale business, or service-based company and want an SaaS-ready PHP ERP script with built-in POS and HR tools.
Don’t buy it if:
You require deep customization, mobile-first experience, or enterprise-grade integration features.
👉 Get ERP Business from CodeCanyon Now
FAQs
1. Can ERP Business be used for SaaS projects?
Yes, but you’ll need to purchase the Extended License for legal SaaS deployment or client billing.
2. Does the script include a POS system?
Yes, a fully integrated POS system is included for retail and billing operations.
3. Can I use it for inventory and accounting together?
Absolutely. ERP Business includes modules for both stock tracking and financial reporting.
4. Is it beginner-friendly?
The script includes an installation wizard, but some technical knowledge may be needed for setup and customization.
5. Are updates and support included?
Yes, free lifetime updates and 6 months of author support are included with your CodeCanyon purchase.




1 thought on “ERP Business Review – A Complete PHP ERP Solution for Shops”