Contents
Summary
HRM Human Resource Management System is a powerful PHP script that helps businesses manage employee data, payroll, attendance, and leaves in one place. Built with Laravel, it’s ideal for startups and SaaS platforms. 👉 Buy HRM on CodeCanyon
What Is HRM Human Resource Management System?
HRM Human Resource Management System is a Laravel-powered PHP script that lets you run a full-featured HR department online. It helps manage employee records, payroll, leaves, attendance, and roles—making it a perfect backend for small businesses, HR SaaS products, or internal tools.
Who It’s For
-
SaaS founders launching HR platforms
-
Developers building HRM for clients
-
Small to medium-sized businesses
-
Agencies or freelancers managing internal HR tools
Key Features of HRM Human Resource Management System
-
Employee management (profiles, roles, departments)
-
Attendance tracking with reporting
-
Leave requests and approval flow
-
Salary and payroll management
-
Shift scheduling
-
Holiday and noticeboard system
-
Role-based access control
-
Built with Laravel framework
-
Clean admin dashboard
-
Multi-user system (admin, HR, employee)
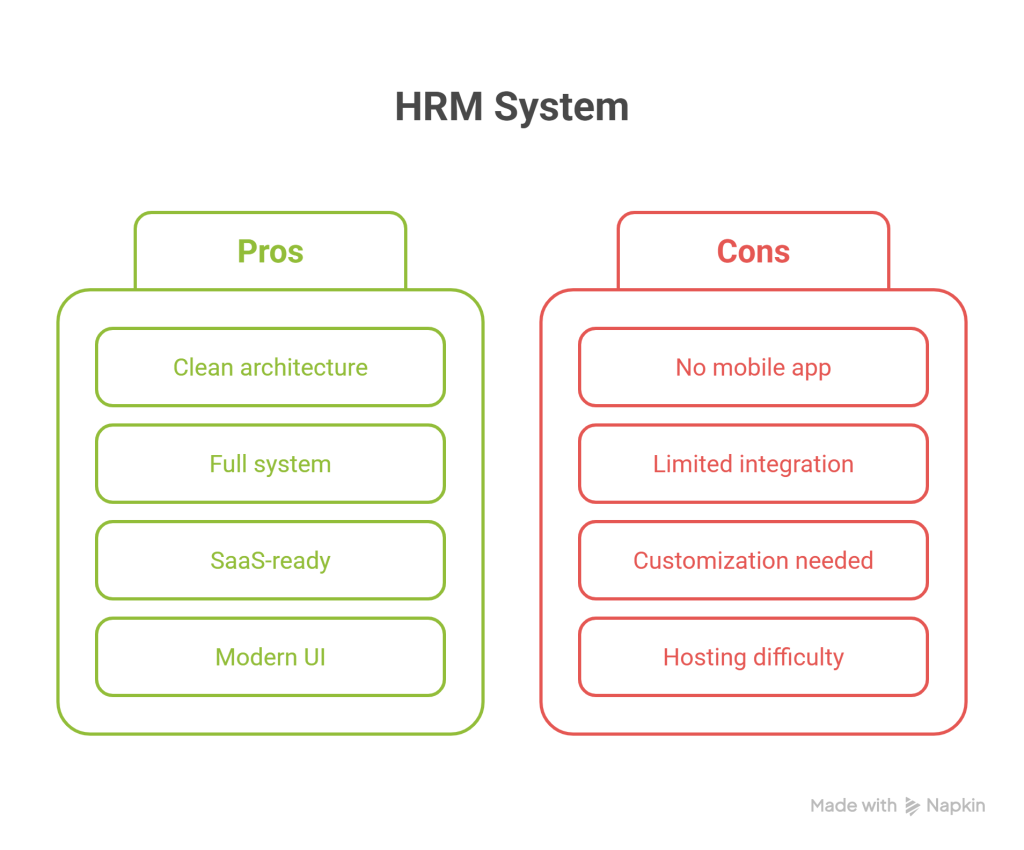
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Clean Laravel-based architecture | No built-in mobile app |
| Full HR, attendance, and payroll system | Limited third-party integration out of the box |
| SaaS-ready PHP script with role management | Advanced reporting requires customization |
| Modern UI and easy-to-use interface | Self-hosting may be difficult for non-technical users |
Installation and Setup Guide
Installation Steps
-
Upload files to your server (via cPanel, FTP, or SSH)
-
Create a new MySQL database
-
Edit
.envfile with DB, mail, and other settings -
Run the installation wizard in browser
-
Configure admin and user roles
-
Add employees and start using modules
System Requirements
-
PHP 8.0 or higher
-
MySQL 5.7+
-
Apache or Nginx web server
-
Laravel support (mod_rewrite enabled)
-
SSL recommended for production
📘 Documentation is included with the script or in the download files on CodeCanyon.
Pricing and License Options
| License Type | Price | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Regular License | $49 | For internal HR use or one client project |
| Extended License | $299 | For SaaS platforms or hosted HR services |
👉 Buy HRM Human Resource Management System on CodeCanyon: https://1.envato.market/xkD99k
Final Verdict – Is It Worth Buying?
HRM is a complete, SaaS-ready PHP script built with Laravel that covers all the essentials of HR operations—from attendance to payroll. The interface is user-friendly, and the modular structure makes customization easy for developers.
Buy this if:
-
You want to build a self-hosted HR tool
-
You’re launching a SaaS HRM product
-
You need a Laravel-based backend with complete HR features
Avoid this if:
-
You’re looking for advanced analytics or integrations (like Slack, Zoom, etc.)
-
You don’t have experience managing PHP hosting or Laravel apps
FAQs
1. Can I use this script for a SaaS HR platform?
Yes, the Extended License allows you to use it as a SaaS solution.
2. Does it support multiple user roles?
Yes, it comes with admin, HR, and employee roles with permission control.
3. Is it built with Laravel?
Yes, HRM is built using the Laravel framework, known for its speed and security.
4. Does it support attendance tracking?
Absolutely. The script includes attendance logs and shift tracking.
5. Is support available?
Support is provided via the CodeCanyon support system by the author.




1 thought on “HRM Human Resource Management System Review – Best PHP Script for HR and Payroll”